Access Control & Smart Cards
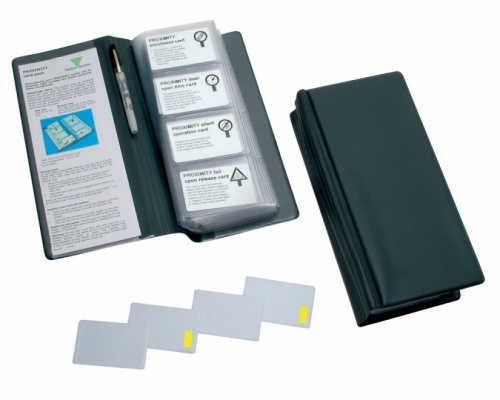
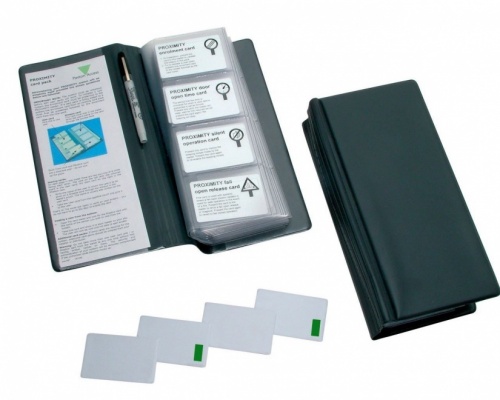
An Access Control Card is a type of ID card that works with an access control system to unlock a door. The cards - sometimes known as contactless cards or proximity cards - are essentially a replacement of the traditional lock and key. In fact they are even more secure than a key, because in the event that a card is ever lost or falls into the wrong hands, it can simply be de-activated to prevent access. Plus it's far more difficult to duplicate an access control card than a traditional key.
Recent advances in ID card technology have made card-based access a popular and trusted method of entry for many different businesses, government bodies and organisations. They are used to secure office buildings and facilities belonging to everything from colleges to care homes to car parks - anywhere that needs a secure, restricted level of entry.
Access control cards work in conjunction with ID card readers located at entrances to buildings or facilities. The user simply swipes or waves their card in front of the card reader, the card reader verifies the information on the card, then access is granted (or denied). These days, the process is near instant. There are several different types of access control card, each one being underpinned by different technologies:
Magstripe cards include a magnetic stripe that holds ID information that's read when the card is swiped. These are a reasonable method of access control but mainly for low risk settings because they are not difficult to duplicate.
Extra security is provided by contactless cards (such as Radio Frequency IDentification (RFID) cards) which transmit their information over the air with no physical contact required between the card and the card reader. RFID cards contain small computer chips which have been programmed to hold ID information. RFID cards come in two 'flavours' - Low Frequency RFID proximity cards which send information one way from the card to the reader, and High Frequency RFID Smart Cards which contain a great deal more technology and require two way communication.